Does Rilassáre's alternative medicine replace traditional medicine?
No, alternative medicine is a supplement to the treatments the patient may already be undergoing and is not contraindicated in any case due to its safety and lack of adverse reactions or side effects. Alternative medicine helps strengthen your immune system and regulates your body's acidity for optimal functioning.
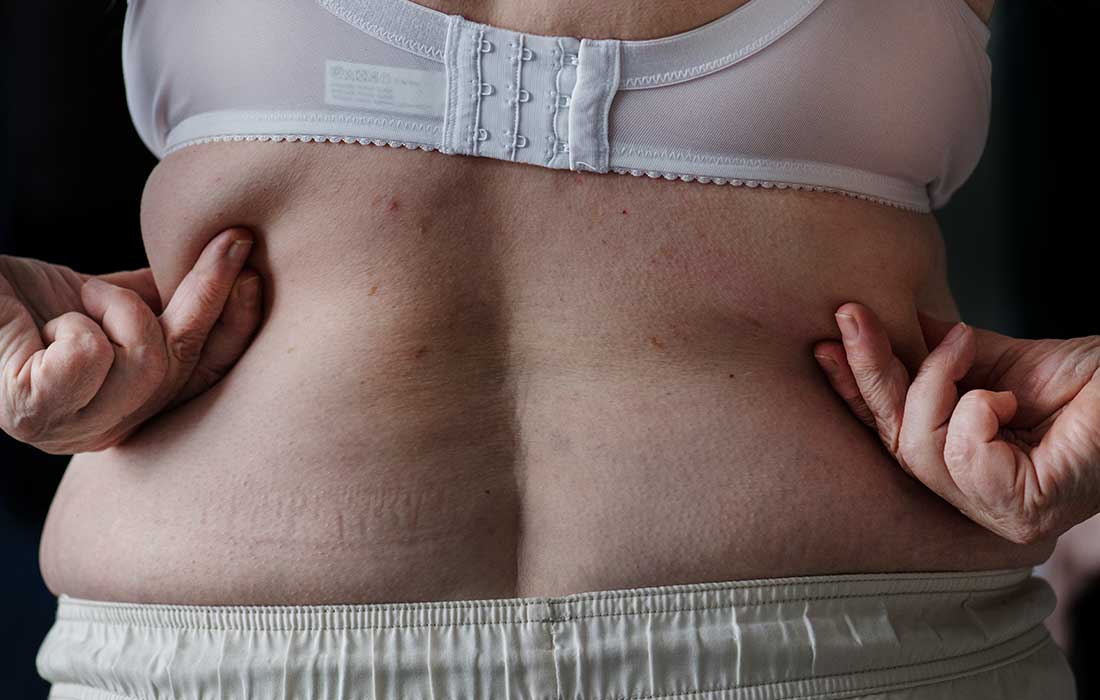
What is obesity?
Obesity is a complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat. It is not just a cosmetic concern. Obesity is a medical problem that increases the risk of other diseases and health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain cancers.
Symptoms of obesity may include:
- • Pain areas. Joints or back.
- • Other common symptoms. Overweight, uncontrolled appetite, fatigue, belly fat, or snoring.
Causes of obesity
Although genetic, behavioral, metabolic, and hormonal influences play a role in body weight, obesity occurs when you consume more calories than you burn through daily activities and exercise. The body stores the excess calories as fat.
In the U.S., most people’s diets are too high in calories—often from fast food and high-calorie beverages. People with obesity may eat more calories before feeling full, feel hungry sooner, or eat more due to stress or anxiety.
Many people in Western countries now have less physically demanding jobs, so they burn fewer calories at work. Even daily activities burn fewer calories thanks to conveniences like remote controls, escalators, online shopping, and drive-through banking.
Types of obesity
Dietary obesity
Predominantly affects the face, neck, back, and chest areas. Caused by excessive unhealthy eating habits. If continued, it can become very dangerous to the body. Symptoms: abnormal body heat and excessive sweating.
Severe dietary obesity is another form that is concentrated mainly in the abdomen, giving a round and disproportionate appearance. Symptoms: excessive heat, bloating, and drowsiness after meals.
Hereditary family obesity
Characterized by fat and cold cellulite accumulating on the outer upper buttocks and warm fat above the pubic area, although it usually doesn't cause significant aesthetic imbalance. This type develops in episodes during critical life stages.
Symptoms: excessive coldness in the buttocks and mild bloating after eating.
Venous circulatory obesity
Occurs in the lower limbs and is genetic in origin. It differs from capillary circulatory obesity as it emerges during pregnancies and involves vein wall swelling and clot formation (phlebitis or periphlebitis).
Capillary circulatory obesity
This type involves invasive fat accumulation in the upper and lower limbs and is linked to genetics. It often begins as cellulite during puberty and can progress to a serious circulatory issue.
Gluteal obesity
Located from the waist to the knees, giving a very distinct appearance, especially on the inner thighs.
Begins in childhood or puberty and worsens with pregnancies, hormonal imbalances, gynecological surgeries, and menopause.
Nervous abdominal obesity
Fat accumulates in the front and center of the abdomen, giving a prominent hexagonal appearance.
Develops during high-stress or depressive periods and appears in sudden episodes. Often a psychosomatic reaction during childhood.
Symptoms: fatigue, a strong craving for sugar between meals, and bloating immediately after eating.
Prediabetic metabolic obesity
Located in the belly and gives a pale appearance. Causes excessive warmth and bloating even with little food intake. Fat builds up suddenly rather than gradually, often during medical treatments, hormonal contraceptive use, or pregnancy.
Atherogenic metabolic obesity
The belly appears round and red but feels locally cold. It is a vascular condition of genetic origin that worsens with alcohol consumption (in both food and drink).
Fat builds up progressively and accelerates without effective intervention. Symptoms: drowsiness and excessive body heat after eating.
Obesity from a sedentary lifestyle
Increasingly common. Fat accumulates like a float ring and appears when physical activity decreases significantly without reducing fat or carbohydrate intake.
Fat has a dense appearance and causes a sensation of excessive heat. Daily physical activity is essential, especially under the guidance of a specialist.
Hypothalamic obesity
Leads to the most morbid forms. Due to a hypothalamic disorder, fat spreads rapidly over the upper body, entire abdomen, hips, and buttocks. Often triggered by emotional shock and linked to depressive episodes.
Symptoms: lack of satiety during meals and other psychosomatic signs.
Reducing this type of obesity requires a combination of medical, surgical, nutritional, and psychological care.
Endogenous cortisol obesity
A hereditary/genetic disease affecting adrenal gland function. It requires urgent treatment by an endocrinology specialist.
Obesity diagnosis
The doctor will check your Body Mass Index (BMI). A BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese. Higher BMI numbers increase health risks further.
Obesity treatments
The main treatment involves lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthier diet and getting regular exercise.
- • Self-care.
- • Physical activity, weight loss, low-carb diet, and low-fat diet.
- • Therapies.
- • Behavioral therapy.
Obesity complications
People with obesity are more likely to develop several potentially serious health problems, including:
- • Heart disease and strokes. Obesity raises the risk of high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels, which are risk factors for heart disease and strokes.
- • Type 2 diabetes. Obesity can affect how the body uses insulin to regulate blood sugar, increasing the risk of insulin resistance and diabetes.
- • Certain cancers. Obesity may raise the risk of uterine, cervical, endometrial, ovarian, breast, colon, rectal, esophageal, liver, gallbladder, pancreatic, kidney, and prostate cancers.
- • Digestive problems. Obesity increases the risk of heartburn, gallbladder disease, and liver problems.
- • Sleep apnea. People with obesity are more likely to have sleep apnea, a serious condition in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
- • Osteoarthritis. Obesity puts extra pressure on weight-bearing joints and promotes inflammation, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis.
- • Severe COVID-19 symptoms. Obesity increases the risk of developing severe symptoms if infected with COVID-19. Severe cases may require intensive care or mechanical ventilation.
Obesity prevention
- • Drink plain water—6 to 8 glasses daily (about 250 ml each).
- • Avoid sodas, juices, or any sugar-sweetened beverages.
- • Be physically active. Adults should aim for 30 minutes daily, while children and teens should aim for 1 hour.
Online Doctor
If you would like an online consultation with one of our doctors, click the button below to visit our website www.virtualmedical.com.mx
Visit Site